写了个一个go的基础组件给团队使用,主要功能是watch到kubernetes中集群中service的状态,针对service对应的pods的变化为对应的pod授权访问到MySQL服务,服务上线后没几天发现出现了CPU使用非常高的情况,所以使用了pprof对整个程序进行了分析。
贴个图片看下,从图中我们可以看到这个程序占用的CPU非常的高,通过strace跟踪进程也没发现异常,进程是处于wait的状态.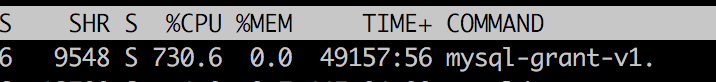
所以这里通过Go pprof分析下到底是在哪里比较耗时。
在分析之前,对于一个go程序而已,我们比较关注的是哪些性能数据呢?我想无非有下面这些
- CPU profile, 报告程序的 CPU 使用情况,按照一定频率去采集应用程序在 CPU 和寄存器上面的数据
- Memory Profile(Heap Profile):报告程序的内存使用情况
- Block Profiling:报告 goroutines 不在运行状态的情况,可以用来分析和查找死锁等性能瓶颈
- Goroutine Profiling:报告 goroutines 的使用情况,有哪些 goroutine,它们的调用关系是怎样的
pprof是什么
pprof其实存在与go语言的2个包中,net/http/pprof和runtime/pprof。
其中:
net/http/pprof是通过提供了一个http的server在应用运行时收集应用画像数据的一个可视化工具。runtime/pprof则是在运行时直接收集应用画像数据的一个可视化工具。
所以,如果你的应用程序是一个常驻的服务的话,需要使用net/http/pprof包,而如果你的应用程序是一个工具型的应用的话,则可以使用runtime/pprof包。
服务型程序pprof的使用
首先在我们程序里引入1
import _ "net/http/pprof"
然后再main函数里加入1
2
3go func() {
log.Println(http.ListenAndServe("localhost:6060", nil))
}()
这时候,我们就可以使用http://localhost:6060/debug/pprof来浏览我们的一些性能数据,如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10/debug/pprof/
profiles:
0 block
31 goroutine
53 heap
0 mutex
10 threadcreate
full goroutine stack dump
通过这个页面,我们可以点击上面的子连接,进入到以下的一些子页面
- /debug/pprof/profile:访问这个链接会自动进行 CPU profiling,持续 30s,并生成一个文件供下载
- /debug/pprof/heap: Memory Profiling 的路径,访问这个链接会得到一个内存 Profiling 结果的文件
- /debug/pprof/block:block Profiling 的路径
- /debug/pprof/goroutines:运行的 goroutines 列表,以及调用关系
应用型程序pprof的使用
首先在程序里引入1
import "runtime/pprof"
然后在main函数中加入1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30var cpuprofile = flag.String("cpuprofile", "", "write cpu profile to `file`")
var memprofile = flag.String("memprofile", "", "write memory profile to `file`")
func main() {
flag.Parse()
if *cpuprofile != "" {
f, err := os.Create(*cpuprofile)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("could not create CPU profile: ", err)
}
if err := pprof.StartCPUProfile(f); err != nil {
log.Fatal("could not start CPU profile: ", err)
}
defer pprof.StopCPUProfile()
}
// ... rest of the program ...
if *memprofile != "" {
f, err := os.Create(*memprofile)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("could not create memory profile: ", err)
}
runtime.GC() // get up-to-date statistics
if err := pprof.WriteHeapProfile(f); err != nil {
log.Fatal("could not write memory profile: ", err)
}
f.Close()
}
}
其实是runtime中的pprof已经为我们提供了收集CPU数据和内存数据的接口,我们只是需要在程序运行的时候,把数据写入到文件中就可以
go tool pprof命令
上面说的收集到的数据写入到文件中,我们可以使用go pprof tool来查看文件里面的数据。
在服务型应用中,我们可以使用
1 | go tool pprof http://localhost:6060/debug/pprof/profile |
来获取CPU的性能数据,或者1
go tool pprof http://localhost:6060/debug/pprof/profile
来或者内存的性能数据。当然还有其他,可以参考文档,这里我们以profile CPU数据为例。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19go tool pprof http://localhost:6060/debug/pprof/profile
Fetching profile over HTTP from http://localhost:6060/debug/pprof/profile
Saved profile in /Users/Johnny/pprof/pprof.samples.cpu.003.pb.gz
Type: cpu
Time: Jul 25, 2018 at 3:09pm (CST)
Duration: 30.11s, Total samples = 48.32s (160.49%)
Entering interactive mode (type "help" for commands, "o" for options)
(pprof) top10
flat flat% sum% cum cum%
8300ms 17.18% 17.18% 8300ms 17.18% runtime.mach_semaphore_signal /usr/local/Cellar/go/1.9.2/libexec/src/runtime/sys_darwin_amd64.s
8000ms 16.56% 33.73% 8000ms 16.56% runtime.mach_semaphore_wait /usr/local/Cellar/go/1.9.2/libexec/src/runtime/sys_darwin_amd64.s
7860ms 16.27% 50.00% 7860ms 16.27% runtime.mach_semaphore_timedwait /usr/local/Cellar/go/1.9.2/libexec/src/runtime/sys_darwin_amd64.s
7850ms 16.25% 66.25% 7850ms 16.25% runtime.kevent /usr/local/Cellar/go/1.9.2/libexec/src/runtime/sys_darwin_amd64.s
2850ms 5.90% 72.14% 4970ms 10.29% runtime.scanobject /usr/local/Cellar/go/1.9.2/libexec/src/runtime/mgcmark.go
1610ms 3.33% 75.48% 1610ms 3.33% runtime.memmove /usr/local/Cellar/go/1.9.2/libexec/src/runtime/memmove_amd64.s
910ms 1.88% 77.36% 910ms 1.88% runtime.usleep /usr/local/Cellar/go/1.9.2/libexec/src/runtime/sys_darwin_amd64.s
810ms 1.68% 79.04% 910ms 1.88% runtime.heapBitsForObject /usr/local/Cellar/go/1.9.2/libexec/src/runtime/mbitmap.go
720ms 1.49% 80.53% 810ms 1.68% runtime.heapBitsSetType /usr/local/Cellar/go/1.9.2/libexec/src/runtime/mbitmap.go
590ms 1.22% 81.75% 590ms 1.22% runtime.memclrNoHeapPointers /usr/local/Cellar/go/1.9.2/libexec/src/runtime/memclr_amd64.s
使用topN命令,我们可以列出前面N条比较耗费CPU的数据,上面我们看到是直接通过http的接口实时的访问数据,也可以通过下载保存好的文件查看里面的数据,比如:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18go tool pprof ./main ~Johnny/pprof/pprof.samples.cpu.003.pb.gz
File: main
Type: cpu
Time: Jul 25, 2018 at 3:09pm (CST)
Duration: 30.11s, Total samples = 48.32s (160.49%)
Entering interactive mode (type "help" for commands, "o" for options)
(pprof) top10
flat flat% sum% cum cum%
8300ms 17.18% 17.18% 8300ms 17.18% runtime.mach_semaphore_signal /usr/local/Cellar/go/1.9.2/libexec/src/runtime/sys_darwin_amd64.s
8000ms 16.56% 33.73% 8000ms 16.56% runtime.mach_semaphore_wait /usr/local/Cellar/go/1.9.2/libexec/src/runtime/sys_darwin_amd64.s
7860ms 16.27% 50.00% 7860ms 16.27% runtime.mach_semaphore_timedwait /usr/local/Cellar/go/1.9.2/libexec/src/runtime/sys_darwin_amd64.s
7850ms 16.25% 66.25% 7850ms 16.25% runtime.kevent /usr/local/Cellar/go/1.9.2/libexec/src/runtime/sys_darwin_amd64.s
2850ms 5.90% 72.14% 4970ms 10.29% runtime.scanobject /usr/local/Cellar/go/1.9.2/libexec/src/runtime/mgcmark.go
1610ms 3.33% 75.48% 1610ms 3.33% runtime.memmove /usr/local/Cellar/go/1.9.2/libexec/src/runtime/memmove_amd64.s
910ms 1.88% 77.36% 910ms 1.88% runtime.usleep /usr/local/Cellar/go/1.9.2/libexec/src/runtime/sys_darwin_amd64.s
810ms 1.68% 79.04% 910ms 1.88% runtime.heapBitsForObject /usr/local/Cellar/go/1.9.2/libexec/src/runtime/mbitmap.go
720ms 1.49% 80.53% 810ms 1.68% runtime.heapBitsSetType /usr/local/Cellar/go/1.9.2/libexec/src/runtime/mbitmap.go
590ms 1.22% 81.75% 590ms 1.22% runtime.memclrNoHeapPointers /usr/local/Cellar/go/1.9.2/libexec/src/runtime/memclr_amd64.s
命令格式是:1
go tool pprof [binary] [source]
binary 是应用的二进制文件,用来解析各种符号;source 表示 profile 数据的来源,可以是本地的文件,也可以是 http 地址
另外,我们可以使用web命令,来生成一个各个方法的调用1
(pprof) web
生成的图片如下: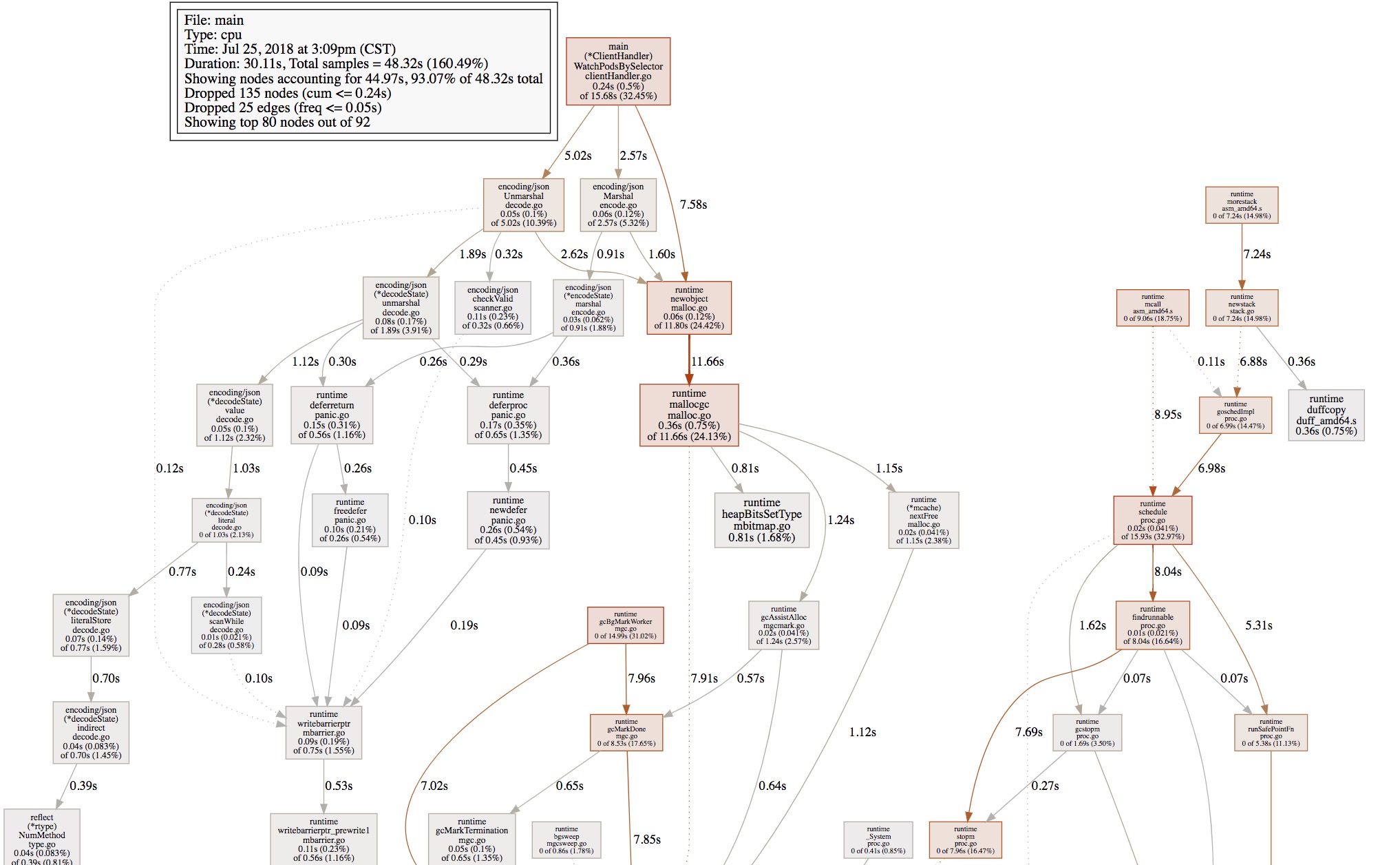
还可以使用list命令,通过正则的方式,查看某个方法的具体调用。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25(pprof) list
command list requires an argument
(pprof) list .WatchPodsBySelector
Total: 48.32s
240ms 15.68s (flat, cum) 32.45% of Total
. . 210: watchPods, err := handler.clientset.CoreV1().Pods(namespace).Watch(metav1.ListOptions{LabelSelector: selector})
. . 211: if err != nil {
. . 212: xLog.Errorf("WatchPodsBySelector watch error: %+v", err)
. . 213: return
. . 214: }
10ms 10ms 215: for {
. . 216: select {
40ms 280ms 217: case wPods := <-watchPods.ResultChan():
90ms 2.69s 218: t, err := json.Marshal(wPods.Object)
10ms 10ms 219: if err != nil {
. . 220: xLog.Errorf("WatchPodsBySelector Marshal wPods.Object error: %+v", err)
. . 221: return
. . 222: }
10ms 7.59s 223: var p v1.Pod
60ms 5.08s 224: err = json.Unmarshal(t, &p)
. . 225: if err != nil {
. . 226: xLog.Errorf("WatchPodsBySelector Unmarshal wPods.Object error: %+v", err)
. . 227: return
. . 228: }
. . 229: switch wPods.Type {
结束
到这里,回到最初的CPU占用过高的问题,发现在watchPodsBySelector中耗时,一直在占用CPU,导致CPU过高,原因是watchPods可能会因为服务器主动的断开导致chan的close。